REFERENCE - |
Glossary of Technology Terms |
This is a collection of other technical terms that you may encounter with regard to technology-related devices such appliances, smartphones, televisions, wearables, etc.
If you don't find what you want to know here, you could try Our Community, or ask one of the Tech Solutions staff at your nearest Noel Leeming store.
If you don't find what you want to know here, you could try Our Community, or ask one of the Tech Solutions staff at your nearest Noel Leeming store.
| Term | Explanation | |||||||
| 2G | 2G is the 2nd generation of wireless mobile telecommunications technology with average data speeds of 40 Kbps in NZ although it is supposed to be capable of 300 Kbps or 0.3 Mbps. It is now only supported by Vodafone and will be discontinued in 2025. | |||||||
| 3G | 3G is the 3rd generation of wireless mobile telecommunications technology with average data speeds of 20 Mbps in NZ although it is supposed to be capable of 42 Mbps. | |||||||
| 4G | 4G is the 4th generation of wireless mobile telecommunications technology with average data speeds of 36 Mbps for 4G/LTE in NZ although it is supposed to be capable of 150 Mbps. | |||||||
| 4K UHD Resolution |
4K UHD or 4K Resolution is often used when referring to an Ultra High Definition video standard known as 2160p. |  |
||||||
| 5G | 5G is the 5th generation of wireless mobile telecommunications technology with average data speeds up to 200 Mbps initially in NZ, but could increase to as much as 100 Gbps over time. | |||||||
| 8K UHD Resolution |
8K UHD or 8K Resolution is often used when referring to an Ultra High Definition video standard known as 4320p. |  |
||||||
| 16K UHD Resolution |
16K UHD or 16K Resolution is often used when referring to an Ultra High Definition video standard known as 8640p. |  |
||||||
| 480i | 480i is one of the Standard Definition (SD) standards, with a frame size of 704 x 480 pixels (337,920 pixels in total) using Interlaced scanning at 60Hz in USA. This format was used by the NTSC system, which used to be the TV standard in the USA and Japan. | |||||||
| 576i | 576i is one of the Standard Definition (SD) standards, with a frame size of 704 x 576 pixels (405,504 pixels in total) using Interlaced scanning at 50Hz in NZ. This format was used by the PAL system, which used to be the TV standard in NZ, Australia and Europe. | |||||||
| 720p | 720p (also known as HD ready) is one of the High Definition (HD) standards, with a frame size of 1280 x 720 pixels (921,600 pixels in total) using Progressive scanning at 50Hz in NZ. | |||||||
| 1080i | 1080i (also known as Full HD) is one of the High Definition (HD) standards, with a frame size of 1920 x 1080 pixels (2,073,600 pixels in total) using Interlaced scanning at 50Hz in NZ. | |||||||
| 1080p | 1080p (also known as Full HD) is one of the High Definition (HD) standards, with a frame size of 1920 x 1080 pixels (2,073,600 pixels in total) using Progressive scanning at 50Hz in NZ. This resolution is commonly used by basic TV sets. | |||||||
| 1296p | 1296p is one of the High Definition (HD) standards, with a frame size of 2304 x 1296 pixels (2,985,984 pixels in total) using Progressive scanning at 30Hz in NZ. This resolution is commonly used by dash cams and similar devices. | |||||||
| 1440p | 1440p (also known as Quad HD) is one of the High Definition (HD) standards, with a frame size of 2560 x 1440 pixels (3,686,400 pixels in total ) using Progressive scanning at 50Hz in NZ. | |||||||
| 2000 | 2000 is one of the Ultra High Definition (UHD) standards, with a frame size of 2048 x 1536 pixels (3,145,728 pixels in total) using Progressive scanning at 24Hz or 60Hz. | |||||||
| 2160p |
2160p is one of the Ultra High Definition (UHD) standards, but it can be confusing because there are two versions.
The "Consumer" version of 2160p (also known as 4K UHD) has a frame size of 3840 x 2160 pixels (8,294,400 pixels in total) using Progressive scanning at 24, 25 or 30fps. This results in an aspect ratio of 1.77:1 (16:9). The "Digital Cinema Initiative" version of 2160p (also known as DCI or C4K) has a slightly larger frame size of 4096 x 2160 pixels (8,847,360 pixels in total) using Progressive scanning at 24fps. This results in a rather strange aspect ratio of ≈1.90:1 (256:135). However, some consumer cameras can output both versions. |
|||||||
| 2540p | 2540p is one of the Ultra High Definition (UHD) standards, with a frame size of 4520 x 2540 pixels (11,480,800 pixels in total) using Progressive scanning at 24Hz or 30Hz. | |||||||
| 4000p | 4000p is one of the Ultra High Definition (UHD) standards, with a frame size of 4096 x 3072 pixels (12,582,912 pixels in total) using Progressive scanning at 24Hz, 30Hz or 60Hz. | |||||||
| 4320p | 4320p (also known as 8K UHD) is one of the Ultra High Definition (UHD) standards, with a frame size of 7680 x 4320 pixels (33,177,600 pixels in total) using Progressive scanning at 60Hz or 120Hz. | |||||||
| 8640p | 8640p (also known as 16K UHD) is one of the Ultra High Definition (UHD) standards, with a frame size of 15360 x 8640 pixels (132,710,400 pixels in total) using Progressive scanning at 60Hz or 120Hz. This is the sort of resolution being used on some of the latest outdoor display screens, some of which are 5 meters high and nearly 20 metres wide. | |||||||
| ADSL | Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line is a type of digital subscriber line (DSL) broadband technology that is used to connect to the Internet. Theoretically it has a maximum download speed of 12 Mbps (12288 Kbps) and an upload speed of 8 Mbps, but these speeds are seldom achieved. It is called asymmetric because the download & upload speeds are not symmetrical (download is faster than upload). See also VDSL. | |||||||
| ADSL2+ | This is an version of ADSL above which has a maximum download speed of 24 Mbps and an upload speed of 8 Mbps, although these speeds are seldom achieved. | |||||||
| AI | Abbreviation for Artificial Intelligence.) | |||||||
| All-In-One Computer | A desktop computer designed for regular use at a single location on or near a desk due to its size and power requirements, but where the computer is integrated into the screen, with a separate keyboard and mouse. | |||||||
| AMOLED | AMOLED is short for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes. It is a type of display technology that is used in smartphones. Super AMOLED is an AMOLED display that has an integrated touch function: Instead of having a layer that recognizes touch on the top of the screen, the layer is integrated into the screen itself. | |||||||
Android
|
Android is a mobile operating system developed by Google, based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open source software, designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. In addition, Google has further developed Android TV for televisions, Android Auto for cars, and Wear OS for wrist watches, each with a specialized user interface. Variants of Android are also used on game consoles, digital cameras, PCs, TVs and other electronics. | |||||||
| Android TV | Android TV is a version of the Android operating system developed by Google and designed for digital media players, set-top boxes, soundbars, and smart TVs. It is claimed that the use of Android makes them smarter than your average smart TV and superceded the old Google TV which has since been relaunched. More info... | |||||||
| Apple TV | Apple TV is a device powered from the mains that you plug into your TV's HDMI port. Using your iPhone or iPad as a remote control, you can use Apple TV to access video content from Netflix, YouTube, Sky Sport NOW, Apple TV+, and other services. | |||||||
| Artificial Intelligence |
A term that refers to the simulation of human intelligence by machines or electronic devices.
Experts have identified four types of AI have been identified, but it is still evolving. 1. Reactive machines that have no memory and are task specific, e.g. search engines, customer loyalty systems. 2. Limited mamory machines become smarter from experience learning as they go, e.g. self-driving cars. 3. Theory of mind machines that are self aware and understand relationships. These do not exist yet. 4. Self aware machines, that understand themselves such that they could replicate. These do not exist yet. |
|||||||
Bluetooth
|
Bluetooth is a wireless communications technology intended to replace cables. It allows short-range connections between two or more Bluetooth-compatible devices such as mobile phones, tablets, headsets or medical equipment. | |||||||
| Broadband | Broadband is a wide bandwidth data transmission technology which transports multiple signals and traffic types, but is most commonly associated with the Internet. The medium can be coaxial cable, optical fibre, radio (mobile using 3G, 4G or 5G) or twisted pair (ADSL, VDSL). | |||||||
BT Plug
|
This type of connector, known as British Telephone Plug (BS6312), is typically used to connect your telephone or modem/router to the telephone wall socket.
In most instances the other end of the cable will have an RJ11 type plug. |
|||||||
| C4K | C4K or Cinema 4K is often used when referring to an Ultra High Definition video standard known as 2160p. | |||||||
| Casting | A term derived from "Broadcasting" used for mirroring an image to another display device, such as a TV. See Google Chromecast. | |||||||
| CAT-5/CAT-5e | Category 5 cable, commonly referred to as CAT-5 or more correctly CAT-5e, is comprised of 4 twisted pair cables for computer networks. The cable standard provides performance of up to 100 MHz and is suitable for most varieties of Ethernet over twisted pair. CAT-5/CAT-5e is also used to carry other signals such as telephony and video. | |||||||
| CAT-6 |
Category 6 cable, commonly referred to as CAT-6, is comprised of 4 twisted pair cables for computer networks and other network physical layers that are backward compatible with the Category 5/5e standards.
Compared with CAT-5 and CAT-5e, CAT-6 features more stringent specifications for crosstalk and system noise. The cable standard also specifies performance of up to 250 MHz compared to 100 MHz for CAT-5/CAT-5e. |
|||||||
| Chromecast | See Google Chromecast. | |||||||
| Crossover Cable | This is normally a short length of RED coloured CAT-5 or CAT-6 cable with an RJ45 connector at each end, or could have a black cable with RED coloured RJ45 connectors. These cables are used to connect two devices together via their network ports WITHOUT using a network hub or switch. These cables cannot be used to connect to a network hub or switch which require an Ethernet cable instead. | |||||||
| DCI | Abbreviation for Digital Cinema Initiative, it is often used when referring to an Ultra High Definition video standard known as 2160p. | |||||||
DE-15
|
A 15-pin connector used for VGA. | |||||||
| Desktop Computer | A desktop computer is a personal computer designed for regular use at a single location on or near a desk due to its size and power requirements. In most instances it consists of a box containing the computer, with a separate screen, keyboard and mouse. | |||||||
| DeX | A contraction of Desktop eXperience, which is a feature included on some Samsung handheld devices that enables users to extend their device into a desktop-like experience by connecting a keyboard, mouse, and monitor. | |||||||
DisplayPort
|
DisplayPort (DP) is a digital display interface developed by a consortium of PC and chip manufacturers and standardized by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). The interface is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a computer monitor, and it can also carry audio, USB, and other forms of data. |
 Click to enlarge |
||||||
| DisplayPort was designed to replace VGA, DVI, and FPD-Link. The interface is backward compatible with other interfaces, such as HDMI and DVI, through the use of either active or passive adapters. | ||||||||
| Dolby Vision | Dolby Vision is one of the HDR video formats. It is similar to HDR 10+ in that it uses dynamic, not static metadata, giving each frame its own unique HDR treatment. But Dolby Vision provides for even greater brightness (up to 10,000 nits) and more colors too (12-bit depth, for a staggering 68 billion colors). There are no 12-bit capable TVs yet, and brightness of that calibre is still at the prototype stage, but Disney have declared their interest, and 10-bit devices are being manufactured by LG, Panasonic, and Sony. | |||||||
DVI
|
The Digital Visual Interface is a video display interface developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG).
The digital interface is used to connect a video source, such as a video display controller, to a display device, such as a computer monitor.
|
|||||||
What is confusing is that there are six versions with different pin combinations and you must ensure that you use the correct one for your device.
|
 |
|||||||
| DVI was developed with the intention of creating an industry standard for the transfer of digital video content, although many manufacturers have preferred to use HDMI instead. Apple, on the other hand, decided on Mini-DVI and Micro-DVI for some of their computers. | ||||||||
| eSIM | An embedded Subscriber Identity/Identification Module is the equivalent of a physical SIM card but in electronic form. Many of the latest mobile phones, smartwatches, tablets, laptops and IoT devices now support eSIM, and some support multiple eSIM profiles. In NZ, eSIM is currently only supported by Spark - Vodafone NZ plan support during 2022, while 2-degrees have not announced any plans. | |||||||
| Ethernet Cable | This is basically a length of CAT-5 or CAT-6 cable (usually black, blue, green or yellow, but NOT red) with an RJ45 connector at each end. These cables are used to connect devices to a network hub or switch, and not to each other. The latter requires a Crossover cable instead. | |||||||
| Fibre | Refers to a cable made up of super-thin filaments of glass or other transparent materials that can carry beams of light. Because a fiber-optic cable is light-based, data can be sent through it at the speed of light by using a laser transmitter to encode the data into pulses of light. The modem at receiving end of the transmission translates the light signals back into data which can be passed to a computer. In NZ, Chorus claim their fibre operates up to 1 Gbps for downloads and 550 Mbps for uploads. | |||||||
| Fibre BASIC | FibreBASIC refers to a standard Fibre installation where the speed depends on your Local Fibre Company. Addresses in Whangarei, Hamilton, Whanganui, New Plymouth, Tokoroa, Hawera, Cambridge, Te Awamutu, Tauranga and Christchurch will have a Fibre service with the ability to deliver speeds up to 30Mbps for downloads and 10Mbps for uploads. The rest of New Zealand will have a service able to deliver up to 50Mbps for downloads and 10Mbps for uploads. | |||||||
| Fibre 100 | Fibre 100 is an extra cost Fibre option from Spark that delivers up to 100Mbps for downloads and 20Mbps for uploads. | |||||||
| Fibre 200 | Fibre 200 is an extra cost Fibre option from Spark that delivers up to 200Mbps for downloads and 20Mbps for uploads. | |||||||
| Fibre MAX | Ultra Fast FibreMAX is the next generation Fibre broadband from Spark that delivers up to 900Mbps for downloads and 400MMbps for uploads. They claim it is the fastest residential Fibre service in NZ (using gigabit technology). In optimal conditions, most users should see between 700Mbps-900Mbps on a speed test, although some connections may achieve even better than this. In order to get the best performance out of your Ultra Fast FibreMAX service, you might need to change the way you connect to the internet, and most importantly you will need to have high specification hardware in your home. | |||||||
| Generative AI | Generative Artificial Intelligence refers to the use of AI to create new content, such as text, images, audio, music, speech, videos, etc. They are powered by a foundation module that has been trained using human-created real-world data, although the quality of that data raises concerns about its reliability. It then uses data from that model to generate content that is similar to the what it has learned. Examples are AlphaCode, Bard, ChatGPT, Claude, Copilot, DALL-E, GPT-4, Synthesia, etc. | |||||||
| Google Chromecast | Google Chromecast is a device that you plug into your TV's HDMI port, powered by a USB cable (included). Using your smartphone or computer as a remote control, you can use Chromecast to access video content from Netflix, YouTube, Hulu, the Google Play Store and other services. Chromecast Ultra is similar to the basic model but can stream 4K resolution, while Chromecast Audio is a variation for audio streaming only. | |||||||
| Google TV |
Google TV was a smart TV platform from Google co-developed by Intel, Sony, and Logitech that was launched in October 2010 with official devices initially made by Sony and Logitech.
It was discontinued in June 2014 and superceded by Android TV. However, in 2020 it was relaunched as Google's new smart TV platform with a user interface that runs on Android devices such as smartphones, TVs and Google Chromecast. While it is similar to Android TV, it has many extra features that make it easier to use, and is often available on higher-spec TVs. More info... |
|||||||
| Guest Access Point |
Most of us have regular visitors to our houses, such as friends, family, pizza delivery guys, etc, and many of them are going to want access to your Wi-Fi at some point.
The normal process would be to hand over the passcode printed on the back of your router, but there's actually a much better option.
A Guest Access Point can be configured on most Wi-Fi Internet routers which you can give a simple easy-to-remember password and in so doing restrict them from accessing other devices on your network. |
|||||||
| HD | Acronym for High Definition which is a term used to describe video images that have a higher resolution and quality than Standard Definition (SD), but not as high as Ultra High Definition (UHD). Beyond that it becomes rather confusing as there are numerous high definition standards, such as 720p, 1080i, 1080p, and 1440p. If your device says it is High Definition, it is a good idea to understand which standard they are referring to. | |||||||
HDMI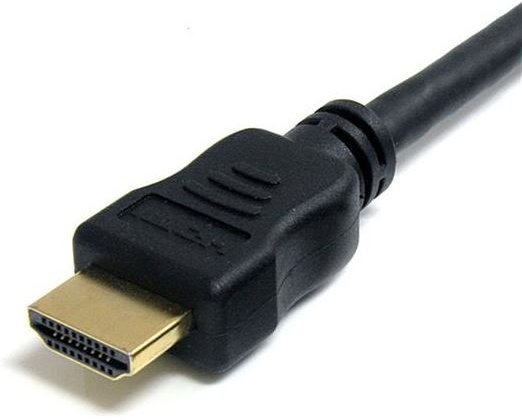 A  C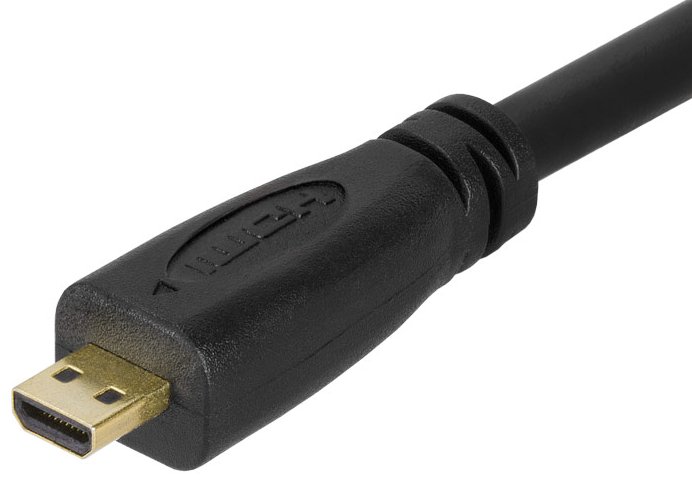  D  E |
The High Definition Multimedia Interface is a proprietary audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed video data and compressed or uncompressed digital audio data from an
HDMI-compliant source device, such as a display controller, to a compatible computer monitor, video projector, digital television, or digital audio device.
(See also DVI.)
There are five connector types: • Type A - Standard connector with 19 pins • Type B - Dual-Link connector with 29 pins but not manufactured • Type C - Mini connector with 19 pins but smaller than Type A • Type D - Micro connector with 19 pins but smaller than Type C • Type E - Automotive connector with 19 pins with an integrated locking tab to guard against vibration HDMI is a digital replacement for analog video standards. Several versions of HDMI have been developed with new functionality and increases in the Maximum Transmission Bit Rate: • HDMI 1.0 (2002) delivers up to 4.95 Gbits/s • HDMI 1.1 (2004) delivers up to 4.95 Gbits/s • HDMI 1.2 (2005) delivers up to 4.95 Gbits/s • HDMI 1.3 (2006) delivers up to 10.2 Gbits/s • HDMI 1.4 (2009) delivers up to 10.2 Gbits/s • HDMI 2.0 (2013) delivers up to 18.0 Gbits/s • HDMI 2.1 (2017) delivers up to 48.0 Gbits/s Through all of these improvements, the connectors have remained the same, but later versions may not work with older cables, so if you are having issues with HDMI, (and this is common) the first step is to try a newer cable. |
|||||||
| HEIC | High Efficiency Image Container (HEIC) is the container or file extension that holds HEIF images or sequences of images, and is only used by Apple. It is the default for images produced using iOS 11 or iPadOS 11 and later, but can be changed from within Settings. | |||||||
| HD Video | High-Definition video is video of higher resolution and quality than standard-definition. While there is no standardized meaning for high-definition, generally any video image with considerably more than 480 vertical lines (NTSC) or 576 vertical lines (PAL) is considered high-definition. |  |
||||||
| This is why you must refer to the HD video mode instead, such as 720p (also known as HD Ready), 1080i or 1080p (also known as Full HD), 1440p (also known as Quad HD), etc. In many cases it will be followed by 50 or 60 denoting the number of frames per second. | ||||||||
| HDR 10 | HDR 10 is the minimum specification for the HDR video formats that allows for a maximum brightness of 1000 nits and a colour-depth of 10 bits. Compared to regular SDR (Standard Dynamic Range), HDR10 allows for an image that is over twice as bright, with a corresponding increase in contrast (the difference between the blackest blacks and the whitest whites), and a colour palette that has one billion shades, as opposed to SDR's 16 million. | |||||||
| HDR 10+ | HDR 10+ is one of the HDR video formats. It is similar to Dolby Vision in that it uses dynamic, not static metadata, giving each frame its own unique HDR treatment. It was developed by three companies (20th Century Fox, Panasonic and Samsung) and increases the maximum brightness to 4,000 nits with increased contrast, but compatible display devices are only being produced by Panasonic and Samsung. It is interesting to note that 20th Century Fox was taken over by Disney in 2019 and the latter have adopted Dolby Vision, so its future may be in doubt. | |||||||
| HDR Video | Acronym for High-Dynamic-Range which is a term used to describe video having a dynamic range greater than that of Standard-Dynamic-Range (SDR) video. HDR capture and displays are capable of brighter whites and deeper blacks. To accommodate this, HDR encoding standards allow for a higher maximum luminance and use at least a 10-bit dynamic range (compared to 8-bit for non-professional and 10-bit for professional SDR video), in order to maintain precision across this extended range. While technically "HDR" refers strictly to the ratio between the maximum and minimum luminance, the term "HDR video" is commonly understood to imply wide colour gamut as well. Since HDR video involves capture, production, content/encoding, and display, even if you purchase an HDR device, it will depend on the content that you watch meeting that standard. Apple iPhone XS and XS Max support HDR. | |||||||
| HLG | Acronym for Hybrid Log Gamma. | |||||||
| HomeKit | HomeKit is a software framework by Apple that lets users configure, communicate with, and control smart-home appliances using Apple devices. By designing rooms, items, and actions in the HomeKit service, users can enable automatic actions in the house through a simple voice command to Siri or through the Home app. | |||||||
| Hybrid Log Gamma |
Hybrid Log Gamma (HLG) is an alternate to HDR video formats, Dolby Vision, HDR10 and HDR10+.
It is the only format that is suitable for broadcast signals and is easily backward compatible because it takes a different approach.
Instead of starting with an HDR signal, HLG begins with a standard dynamic range (SDR) signal that any TV can use. The extra information for HDR rendering is added on, so an HDR TV that knows to look for this information can use it to display a broader range of colours and a wider range of brightness. To get a little more technical, HLG uses the same gamma curve that an SDR signal uses but adds a logarithmic curve with extra brightness over the top of the signal, hence the "log" and "gamma" in HLG. While compatible devices are available in NZ, no HLG signals are broadcast in NZ at this time. An HLG trial started in Australia in July 2018, while the UK and Japan also have plans to broadcast it. |
|||||||
| iMessage | iMessage is a messaging app for Apple devices. If the recipient does not have an Apple device, the message will default to SMS which appears as a green bubble on the sending device as opposed to the blue bubble denoting an Apple device. | |||||||
| Interlaced Scanning | Used when discussing video images where only the even or odd lines of the image frame are redrawn whenever it is refreshed, as distinct from Progressive Scanning. Interlaced Scanning requires 2 cycles to refresh an image and as a result may result in some flicker. | |||||||
| iOS | iOS (formerly iPhone OS) is a mobile operating system created and developed by Apple Inc. that powers many of the company's mobile devices, including the iPhone, iPad, and iPod Touch. | |||||||
| IoT |
The Internet of Things is the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors,
actuators, and connectivity which enables these objects to connect and exchange data.
Because security can be an issue with many of these devices, connect them to your WiFi via the Guest port so that they cannot access your other computers, phones, etc on your local network. |
|||||||
| IPS | Short for In-Plane Switching, it is an LCD technology that was first introduced in 1996 by Hitachi. It was initially developed to correct the poor viewing angles and colour problems that LCDs had at the time. IPS was subsequently improved and refined, leading to Apple adopting it for their iPads. | |||||||
| Laptop Computer | A laptop computer is a personal computer designed for portability, with the computer, screen, keyboard and mousepad in one integrated unit. Because they are designed to be portable, they have rechargeable batteries that are charged from the mains, so can operate from either power source. | |||||||
Lightning
|
|
|||||||
| Using 8 pins instead of 30, Lightning is a more compact version of the older 30-pin connector, which was integrated with devices like the iPhone 4 and the iPad 2. The lightning cable may be inserted into the female port using either side. Without an adapter, it is incompatible with cables and peripherals designed for its predecessors. Frequently offered in MFI and non-MFI versions. | ||||||||
| MFi | This is an acronym for "Made For iPhone/iPod/iPad" and refers to a licensing program for developers of hardware and software peripherals that work with Apples's iPhone, iPod and iPad devices. Often, peripherals such as Lightning cables, will be offered in MFi and non-MFi versions, the latter usually being considerably cheaper because no fee has been payable to Apple, but they may have limitations when it comes to compatibility and reliability - you have been warned. | |||||||
Micro-DVI
|
Digital Visual Interface is a video display interface developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG),
but Micro-DVI is one of the variations that Apple adopted for some of its MacBook Air devices, but without the audio output.
It was replaced by the Mini DisplayPort connector soon after.
|
|||||||
| micro-LED | Also known as micro-LED, mLED or µLED, it is an emerging flat-panel display technology. microLED displays consist of arrays of microscopic LEDs forming the individual pixel elements. When compared with widespread LCD technology, microLED displays offer better contrast, response times, and energy efficiency. | |||||||
Micro SD Card
|
Micro SD cards are flash memory cards which are used in numerous portable electronic devices, such as digital cameras, smartphones, etc to store information. They are considerably smaller than the standard SD card, but can be used in place of one using an adapter. Details about the specification coding written on the cards can be found under SD card. |
|||||||
Mini DisplayPort
|
The Mini DisplayPort (MiniDP or mDP) is a miniaturized version of the DisplayPort audio-visual digital interface that was announced by Apple in October 2008,
and adopted by several hardware vendors, before Apple switched to using USB-C instead.
|
|||||||
Mini-DVI
|
Digital Visual Interface is a video display interface developed by the Digital Display Working Group (DDWG),
but Mini-DVI is one of the variations that Apple adopted for some of its PowerBook G4 devices.
It was replaced by the Mini DisplayPort connector on later models.
|
|||||||
Mini SD Card
|
Mini SD cards are flash memory cards which are used in numerous portable electronic devices, such as digital cameras, smartphones, etc to store information. They are slightly smaller than the standard SD card, but can be used in place of one using an adapter. Details about the specification coding written on the cards can be found under SD card. |
|||||||
| MMS | Multimedia Messaging Service is an enhancement of the standard SMS message that allows you to send up to 1600 characters in your message as well as send GIF, PNG, JPG/JPEG, MP3, or MP4 files. Because of their increased size, they generally cost more to send. To receive MMS messages on an Android device, MMS must be configured under Mobile networks to use saved access points. | |||||||
| Motion Blur |
Motion Blur is the apparent streaking or jerking of moving objects in a video image.
It results when the subject moves faster than consecutive frames, due to rapid movement or slow Refresh Rate.
To overcome this, many TV manufacturers have increased refresh rates that try to address the Motion Blur, and coined confusing new terms for the process. However, not everyone likes it and many turn it off citing the "soap opera" effect. • Bang & Olufsen refers to TruMotion (Eclipse) • LG refers to TruMotion 120 (RR60Hz),TruMotion 240 (RR120Hz) • Panasonic refers to Intelligent Frame Creation • Samsung refers to Motion Rate as in MR120 (RR60Hz) • Sharp refers to Fine Motion or AquoMotion • Sony refers to MotionFlow XR 240 (RR60Hz),XR1440 (RR120Hz) but more recent devices have X-Motion Clarity • TCL refers to Clear Motion Index as in 60/120Hz CMI • Toshiba refers to ClearScan or MEMC • Vizio refers to Effective Refresh Rate with a Clear Action number which doesn't seem to make a lot of sense. If you would like to explore this subject further, check out this site. |
|||||||
| Neo QLED | This is an improvement over the existing QLED displays based on Samsung's quantum dot technology. The biggest difference between the two is that QLED panels use traditional LED backlighting, whereas Neo QLED uses mini-LED backlighting. As the name suggests, mini-LEDs are much smaller than conventional LEDs, meaning you can fit more of them and group them into several dimming zones. | |||||||
| Nit | The Nit is the standard unit of luminance used to describe various sources of light. A higher Nit value means a brighter display. 200 Nits is the equivalent of about 685 ANSI Lumens. Displays for laptops and mobile devices are typically between 200 and 300 Nits, while some smartphiones and tablets are now approaching 500 Nits. Meanwhile Dolby Vision based developments are promising up to 10,000 Nits for large LED screens. | |||||||
| OLED | An organic light-emitting diode (OLED or Organic LED), also known as an organic EL (organic electroluminescent) diode, is a light-emitting diode (LED) in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compound that emits light in response to an electric current. This organic layer is situated between two electrodes; typically, at least one of these electrodes is transparent. OLEDs are used to create digital displays in devices such as television screens, computer monitors, portable systems such as smartphones, handheld game consoles and PDAs. A major area of research is the development of white OLED devices for use in solid-state lighting applications. It is often criticised for its lack of brightness and reliable colour. | |||||||
| Personal Computer or PC | A personal computer is a computing device that is designed to be used by only one user at any one time, although the term often refers to Desktop Computers. | |||||||
| Power Bank | A power bank is essentially a portable charger. Power banks are most commonly used to charge cell phones but are often also used to charge laptops, speakers, and various other chargeable devices. A power bank is a special battery-powered device that uses sophisticated electronics to manage taking in charge from a charger, storing it in a battery, and then using that to charge other devices. Although they are more expensive, the Lithium-Polymer power banks are safer, charge faster and don't their charging capacity over time, as the Lithium-Ion units do. It is important to match the output from the Power Bank to any device that you want to charge from it otherwise damage may occur. | |||||||
| Progressive Scanning | Used when discussing video images where the complete image frame is redrawn whenever it is refreshed, as distinct from Interlaced Scanning. | |||||||
| PUK |
PUK is an abbreviation for Personal Unblocking Key which is a number stored on the SIM card of your mobile device.
If you've entered your SIM card PIN incorrectly more than three times, it will be locked and you'll need the PUK number to unlock it.
Be very careful when entering the PUK number. If you enter this incorrectly more than 7 times, your SIM card will be permanently disabled and you'll need to get a new one. It therefore pays to keep your PIN and PUK in a safe place in case you need to use them, which is typically after something has gone wrong. |
|||||||
| QLED | This is a display device that uses Quantum Light Emitting Diodes, semiconductor nanoparticles to super-charge its brightness and colour. The technology was introduced by Sony on 2013, but has since been licensed by Samsung, Vizio, Hisense and TCL. As cool as quantum dots are, a QLED TV still produces light more or less the same way as a regular LED TV. By using a backlight made up of hundreds (or in some cases thousands) of LEDs, which sits behind a traditional LCD panel, it's these LEDs that give LED (and QLED) its name. | |||||||
| QD-OLED | This is a display device that uses Quantum Dots (QD), semiconductor nanocrystals which can produce pure monochromatic red, green, and blue light. Photo-emissive quantum dot particles are used in a QD layer which converts the backlight to emit pure basic colours which improve display brightness and colour gamut by reducing light losses and colour crosstalk in RGB color filters. This technology is used in LED-backlit LCDs, though it is applicable to other display technologies which use color filters, such as white or blue/UV OLED or microLED. LED-backlit LCDs are the main application of quantum dots. Expect to see the first devices using these displays to be available from Samsung around 2021. | |||||||
| QHD | Acronym for Quad High Definition screen which is another name for 1440p screen resolution. | |||||||
| QNED | This is a display device that uses quantum nano emitting diodes (GaN nanorods) instead of OLED's. It is understood to be similar to QD-OLED technology, but is designed to address some of the OLED's deficiencies. Expect to see the first devices using these displays to be available from Samsung around 2023. | |||||||
| Refresh Rate | The Refresh Rate (RR) refers to the number of image frames that a television can show per second. It is measured in Hertz, which is a unit of frequency. A TV with a 50Hz refresh rate can display 50 images per second, 100Hz displays 100 images/sec, and so on. | |||||||
| Ring | Ring Inc. is a home security and smart home company owned by Amazon. Ring manufactures a range of home security products that incorporate outdoor motion-detecting cameras, including its flagship Ring Video Doorbell and its Neighbors app. Make sure you understand the security issues and implications before installing these devices. | |||||||
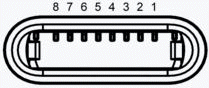
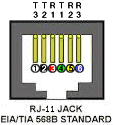
RJ11
|
|
|||||||
|
RJ14 |
see RJ11. | |||||||
|
RJ25 |
see RJ11. | |||||||
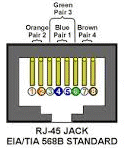
RJ45
|
|
|||||||
| SD | Acronym for Standard Definition which is a term used to describe video images that have a resolution that is not considered to be High or Enhanced Definition, and generally refers to the older standards, such as 480i and 576i, which were the original 4:3 aspect ratio TV formats which were measured in lines rather than pixels. | |||||||
SD Card
Enlarged example showing the various codes: 
|
Secure Digital or SD cards are flash memory cards which are used in numerous portable electronic devices, such as digital cameras, smartphones, etc to store information.
It is important that you choose the correct version for your particular device, which can be rather tricky sometimes, given that there are also two smaller sizes called Mini SD and Micro SD,
and most of the specification criteria is specified using codes.
They are available is a range of capacities: SD: Up to 2 GB; SDHC: over 2 GB to 32 GB; SDXC: over 32 GB to 2 TB; SDUC: over 2 TB to 128 TB. There is also a range of read/write speeds: Standard: 12.5 MB/s; High-speed: 25 MB/s; UHS-I  : 50 MB/s or 104 MB/s; : 50 MB/s or 104 MB/s;UHS-II  : 156 MB/s full-duplex, or 312 MB/s half-duplex; : 156 MB/s full-duplex, or 312 MB/s half-duplex;UHS-III  : 312 MB/s full-duplex, or 624 MB/s half-duplex; : 312 MB/s full-duplex, or 624 MB/s half-duplex;Express  : ≥ 985 MB/s full-duplex. : ≥ 985 MB/s full-duplex.
In addition there is a range of Speed Classes: Class 2 (C2)  : 2 MB/s; : 2 MB/s;Class 4 (C4)  : 4 MB/s; : 4 MB/s;Class 6 (C6)  : 6 MB/s; : 6 MB/s;Class 10 (C10)  : 10 MB/s. : 10 MB/s.
And just to confuse, there is also a range of Video Speed Classes: Class 6 (V6) 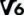 : 6 MB/s suitable for 4K video; : 6 MB/s suitable for 4K video;Class 10 (V10)  : 10 MB/s suitable for 4K video; : 10 MB/s suitable for 4K video;Class 30 (V30) 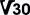 : 30 MB/s suitable for 8K video; : 30 MB/s suitable for 8K video;Class 60 (V60) 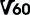 : 60 MB/s suitable for 8K video; : 60 MB/s suitable for 8K video;Class 90 (V90) 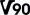 : 90 MB/s suitable for 8K video. : 90 MB/s suitable for 8K video.
Finally, there is also a range of Application Performance Classes: Class 1 (A1)  : 1500 Read IOPS and 500 Write IOPS; : 1500 Read IOPS and 500 Write IOPS;Class 2 (A2)  : 4000 Read IOPS and 2000 Write IOPS. : 4000 Read IOPS and 2000 Write IOPS.
You will also encounter names like Extreme, Plus, Pro, Ultra, etc which are all marketing hype and don't substitute for the codes. Confused? The retailers are as well, so when buying ask for one of the SD cards recommended by the manufacturer for your device. |
|||||||
| SDR Video |
Acronym for Standard-Dynamic-Range which is a term used to describe video images that have a conventional gamma curve, and therefore presenting a dynamic range that is considered standard,
as opposed to High-Dynamic-Range (HDR) video.
The conventional gamma curve was based on the limits of the cathode ray tube (CRT) which allows for a maximum luminance of 100 cd/m2. The first CRT television sets were manufactured in 1934 and the first colour CRT television sets were manufactured in 1954, so the standard is rather outdated when compared to what modern technology can deliver. |
|||||||
SIM Card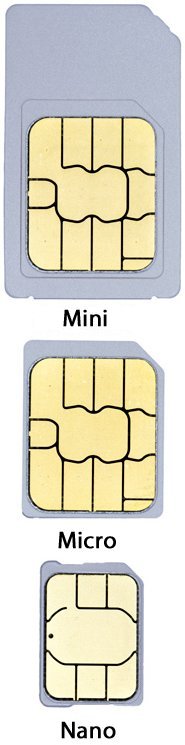
|
A Subscriber Identity/Identification Module is an integrated circuit that is intended to securely store an international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key,
which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephony devices.
SIM cards can also be used in satellite phones, smart watches, computers, security devices and cameras.
Moreover, some smartphones have provision for two SIM cards which can be very useful when travelling overseas.
It should be noted that many of the latest devices now utilise eSIM instead or in addition.
Every SIM card contains its unique serial number (ICCID), an International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) number, security authentication and ciphering information, temporary information related to the local network, a list of the services the user has access to, and two passwords: a Personal Identification Number (PIN) for ordinary use, and a Personal Unblocking Key (PUK) for PIN unlocking. It is also possible to store contact information on many SIM cards. SIM cards are transferable between different mobile devices. The SIM circuit is part of the function of a universal integrated circuit card (UICC) physical smart card, which is usually made of PVC with embedded contacts and semiconductors. The first UICC smart cards were the size of credit and bank cards; sizes were reduced several times over the years (to Mini, Micro, then Nano), usually keeping electrical contacts the same, so that a larger card could be cut down to a smaller size. |
|||||||
SmartThings
|
SmartThings is a software framework by Samsung that lets users configure, communicate with, and control smart-home appliances using Android devices. SmartThings works with a wide range of connected devices, including apppliances, lights, cameras, locks, thermostats, sensors, and more. | |||||||
| Smart TV |
Smart TV is a traditional television set with integrated Internet and interactive Web 2.0 features, which allows users to stream music and videos, browse the internet, and view photos,
but should not be confused with Internet TV, IPTV, or streaming television.
When you consider buying any "smart" product, which is any device that has the ability to connect to the internet, security should always be a top concern. Every internet-ready device contributes to the Internet of Things, which is arguably one of the worst security nightmares today. A major security problem with smart TVs is a lack of updates. Every platform is dependent on its provider for app and OS updates. If you have a TV that no longer receives updates, or takes a long time to receive software patches, your TV could be a vulnerable point on your network. |
|||||||
| SMS | Short Message Service is a text messaging service component of most telephone, Internet, and mobile device systems. It uses standardised communication protocols to enable mobile devices to exchange short text messages up to 160 characters. An intermediary service can facilitate a text-to-voice conversion to be sent to landlines. | |||||||
Tablet
|
A tablet or tablet computer, is a mobile computing device designed to be held in one or two hands.
It typically has a touch-sensitive screen the size of a hardcover book that resembles an over-sized smartphone.
Some even come with a detachable or foldaway keyboard.
The latter are often called 2-in-1 devices because they can also operate like a laptop, or 3-in-1 devices if they can also be connected to an external monitor.
Common examples are Amazon's Fire, Apple's iPad, Lenovo's Yoga, Microsoft's Surface, Samsung's Galaxy Tab range, etc. |
|||||||
| Text Messaging |
Text messaging, or texting, is the act of composing and sending electronic messages, typically consisting of alphabetic and numeric characters, between two or more users of mobile devices, desktops, laptops,
or other type of compatible computer. Text messages may be sent over a cellular network, as well as via satellite or Internet connection. The term originally referred to messages sent using SMS, but also covers MMS and iMessage, although many Internet apps such as Facebook Messenger, Telegram, WeChat and WhatsApp are often included but are better known as "Over The Top" (OTT) applications by definition because they rely on the Internet. |
|||||||
Thunderbolt
 Thunderbolt 1 & 2
Thunderbolt 1 & 2
 Thunderbolt 3 & 4
Thunderbolt 3 & 4
|
Thunderbolt is the brand name of a hardware interface for the connection of external peripherals to a computer.
It has been developed by Intel, in collaboration with Apple, and was initially marketed under the name Light Peak in 2011. Thunderbolt combines PCI Express (PCIe) and DisplayPort (DP) into two serial signals, and additionally provides DC power, all in one cable. Up to six peripherals may be supported by one connector through various topologies. Thunderbolt 1 and 2 use the same connector as Mini DisplayPort (MDP), whereas Thunderbolt 3 and 4 reuse the USB-C connector from USB. |
|||||||
| UHD/Ultra HD | Acronym for Ultra High Definition which is a term used to describe video images that have a higher resolution and quality than standard HD. Current UHD standards are 4K UHD, 8K UHD, and 16K UHD, but some devices are producing images in 6K UHD in a variety of aspect ratios. Beyond that it becomes rather confusing, as there are numerous high definition standards, such as 2000, 2160p, 2540p, 4000p, 4K, 4320p, 8K, 16K, etc. | |||||||
| USB-A | USB-A, formally known as USB Type-A, is distinguished by its flat rectangular slotted connector, but there are two versions. | |||||||
|
||||||||
| USB-B | USB-B, formally known as USB Type-B, is distinguished by its squarish shape with slightly bevelled top corners, but there are two versions. | |||||||
|
||||||||
USB-C
|
||||||||
USB Micro-A
|
|
|||||||
|
USB Micro-AB |
|
|||||||
USB Micro-B

|
USB Micro-B, formally known as Micro USB Type-B, comes in two versions - one for USB 2.0 and another for USB 3.0. | |||||||
|
||||||||
USB Mini-A
|
|
|||||||
|
USB Mini-AB |
|
|||||||
USB Mini-B
|
|
|||||||
| VCSEL | Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser is a semiconductor-based laser diode that emits light or optical beam vertically from its top surface. VCSEL is an emerging technology for many applications including chip to chip interconnect, touchless sensing and gesture recognition. It is expected to make it way to smartphones in the near future for camera focusing, 3-D mapping, and other applications. | |||||||
| VDSL | Very High Speed Digital Subscriber Line is a type of digital subscriber line (DSL) broadband technology that is used to connect to the Internet. It is faster and more reliable than ADSL because it is uses fibre to get broadband to a cabinet near your home and then the copper network from the cabinet to your house. Theoretically it has a maximum download speed of 70 Mbps and an upload speed of 10 Mbps, but these speeds are seldom achieved. It can only be installed if there is a cabinet that is close to your home, i.e. within 1200 metres. | |||||||
VGA
|
A Video Graphics Array connector is a three-row 15-pin DE-15 connector, and was provided on many video cards, computer monitors, laptop computers, projectors, and high definition television sets. On laptop computers or other small devices, a mini-VGA port was sometimes used in place of the full-sized VGA connector. |  |
||||||
| Many devices still include VGA connectors, although it generally coexists with DVI as well as the newer and more compact HDMI and DisplayPort interface connectors that have almost replaced VGA. | ||||||||
| Virtual Reality | Virtual reality is an artificial environment that is created with software and presented to the user in such a way that the user suspends belief and accepts it as a real environment. On a computer, virtual reality is primarily experienced through two of the five senses, sight and sound, and often utilises a VR head set many of which use a smartphone display. | |||||||
| watchOS | watchOS is the mobile operating system of the Apple Watch, developed by Apple Inc. It is based on the iOS operating system and has many similar features. | |||||||
| WearOS | WearOS a version of Google's Android operating system designed for smartwatches and other wearables. | |||||||
| Wi-Fi Versions |
Wi-Fi is a technology that allows computers and other devices to communicate via a wireless signal, while the speed is dependent on the Wi-Fi standard used by each device.
If your device wil not connect, you may have a compatibility issue associated with the following standards as defined by the WiFi Alliance. • IEEE 802.11 released in 1997 is now defunct and will no longer work. • IEEE 802.11a released in 1999 works on the 5GHz band with a maximum data rate of 54 megabits per second, but is subject to interference so range is typically poor. • IEEE 802.11b released in 1999 works on the 2.4GHz band with a maximum data rate of 11 megabits per second. • IEEE 802.11g released in 2003 works on the 2.4GHz band with a maximum data rate of 54 megabits per second. • IEEE 802.11n released in 2009 works on the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands with a maximum data rate of 600 megabits per second. • IEEE 802.11ac released in 2013 works on the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands with a maximum data rate of 600 megabits per second. • IEEE 802.11ad released in 2013 works on the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands with a maximum data rate of 600 megabits per second. • IEEE 802.11af released in 2013 works on the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands with a maximum data rate of 600 megabits per second. • IEEE 802.11ah released in 2013 works on the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands with a maximum data rate of 600 megabits per second. • IEEE 802.11ai released in 2013 works on the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands with a maximum data rate of 600 megabits per second. • IEEE 802.11aj is a rebranding of 801.11ad that works on 45GHz for use in special regions such as China. • IEEE 802.11aq released in 2013 works on the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands with a maximum data rate of 600 megabits per second. • IEEE 802.11ax released in 2018 is the successor to 802.11ac and works on the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands with a maximum data rate of 10.53 Gigabits per second. † During 2019, a new standard based on IEEE 802.11ax was released called WiFi CERTIFIED 6 (or simply WiFi 6) with enhanced modulation and up to 25% faster data transmission. ‡ During 2020, another standard based on IEEE 802.11ax was released called WiFi CERTIFIED 6E (or simply WiFi 6E) with enhanced bandwidth by using the 6GHz frequency but very few devices support it at this time - maybe by end of 2021. • IEEE 802.11ay as of January 2021 is still in development and will work on 60GHz with a proposed maximum data rate of 20 gigabits per second. • IEEE 802.11be as of January 2021 is still in development and will work on 60GHz with a proposed maximum data rate of 20 gigabits per second, but with stationary and pedestrian speeds in the 2.4GHz, 5GHz and 6GHz frequency bands. |
|||||||
| WQHD | Acronym for Wide Quad High Definition screen which is another name for 1440p screen resolution. | |||||||
| WUXGA | Acronym for Widescreen Ultra eXtended Graphics Array, which describes a display device with a resolution of 1920 x 1200 pixels. | |||||||